Drifting buoys - DBCP
What is a drifting buoy?
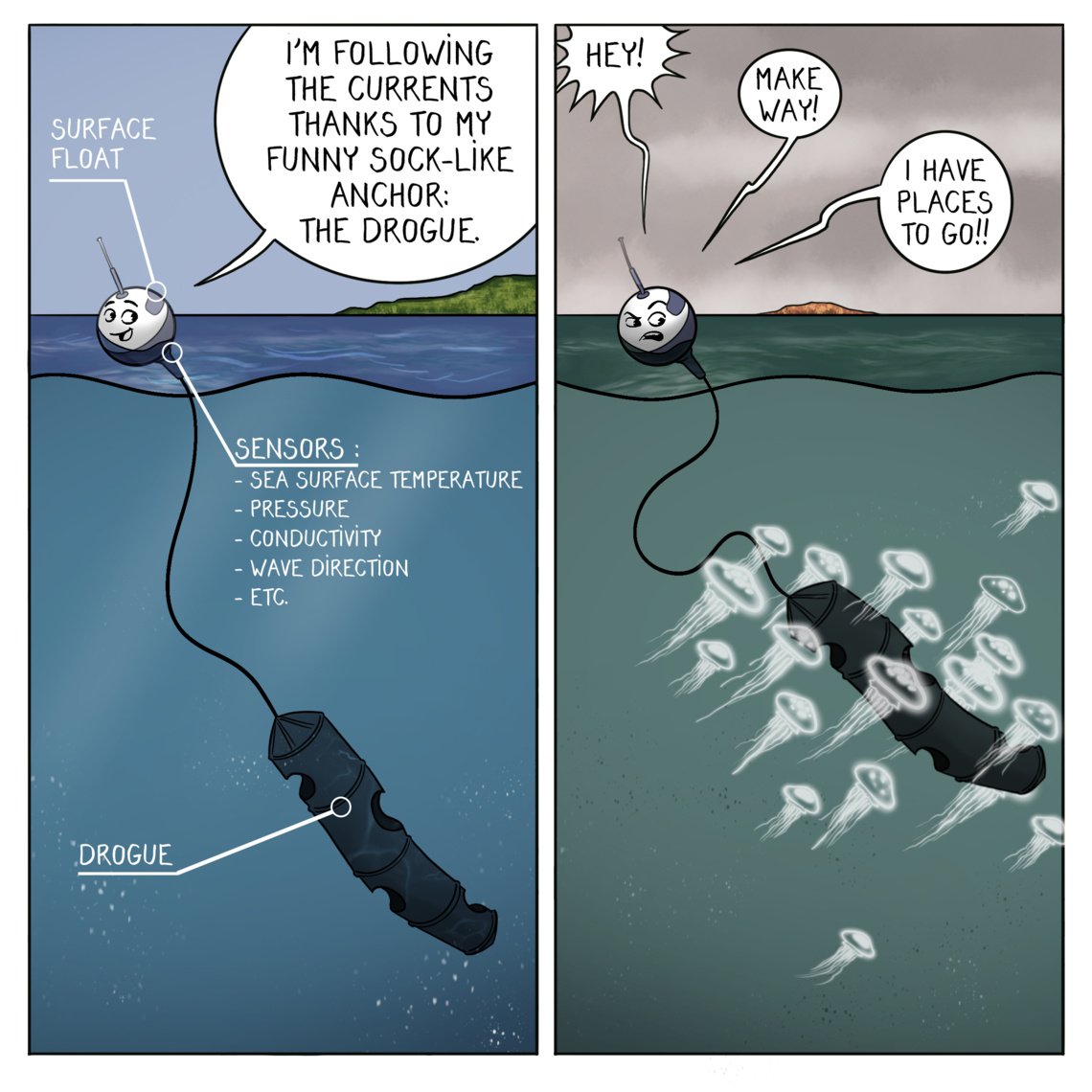
Drifting buoys are floating ocean buoys equipped with meteorological and oceanographic sensors and a floating anchor. They are part of the Data Buoy Cooperation Panel (DBCP) international program. Buoys are deployed by research vessels, commercial ships, ocean sailors, and volunteer mariners.
How does it work?
Drifting buoys are equipped with sensors on the surface hull. They also have an anchor - called a drogue - centred at 15m below the surface, so that the buoys follow the water circulation and are not influenced by the wind.
Drifting buoys are usually equipped with barometers to measure atmospheric pressure. They also collect atmospheric and surface ocean temperature, wind speed and ocean surface salinity.
They all have satellite communications equipment to transmit their observations and information on their position in real-time.
Atmospheric pressure is the air pressure in a specific location. Low air pressure is called a depression and usually comes with rain.
Salinity measures how much salt is present in the sea water.
Conductivity measures a material's ability to conduct an electric current. In the sea, it is linked to how much salt there is.
What kind of ocean observations are collected?
- Sea surface temperature
- Atmospheric pressure
- Wind direction and speed
- Conductivity > Salinity
- Wave direction
What are the observations helping with?
Here are some examples of how the information gathered can be used.
Operational services
Drifting buoys provide information useful for global to regional weather forecasts, including extreme events, marine forecasts, monitoring ocean circulation (currents, tides, waves, etc.) and feeding data models of the ocean.
Their observations are also valuable for assisting fisheries and ensuring safety at sea, for example during search and rescue operations.
Climate change
The observations are used for climate research, ocean monitoring and prediction. They are notably useful for tracking the way El Niño and La Niña, two climate events occurring in the Pacific Ocean, influence global ocean currents, or how a warmer climate affects the path of major ocean currents.
Where can we find it?
Drifting buoys are deployed in high seas in every ocean.
Drifting buoys key numbers
- Number of buoys: 1,500
- Buoy lifetime: 1 year to 18 months
- DBCP starting year: 1985
Learn more about drifting buoys
Lagrangian drifters were first designed and deployed in the world ocean in the context of the Surface Velocity Program (SVP) of the World Ocean Circulation Experiment (WOCE) and the Tropical Ocean and Global Atmosphere Program (TOGA), which eventually became the Global Drifter Array.
These SVP drifters were standardized in 1991. In 1993, drifting buoys with barometer ports, called SVP-B drifters, were tested in the high seas and proven to provide reliable surface air pressure measurements.
If you want to learn more about this program, visit the DBCP website.